
Trabalhando com API em JavaScript com Método Fetch
No desenvolvimento web moderno, o uso de APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) se tornou fundamental para criar aplicações dinâmicas e interativas. JavaScript, sendo uma das linguagens de programação mais populares, oferece diversas ferramentas e métodos para trabalhar com APIs de maneira eficiente.
O que é uma API?
Uma API, ou Interface de Programação de Aplicações, é um conjunto de regras que permite que diferentes sistemas de software se comuniquem entre si. No contexto do desenvolvimento web, APIs frequentemente são usadas para permitir que um frontend (a parte visível de uma aplicação) se comunique com um backend (a parte oculta que processa dados e lógica de negócios).
Uma das maneiras mais comuns de fazer requisições HTTP em JavaScript é utilizando a função fetch. Introduzida no ECMAScript 6, fetch oferece uma interface moderna e flexível para trabalhar com APIs.
Exemplo
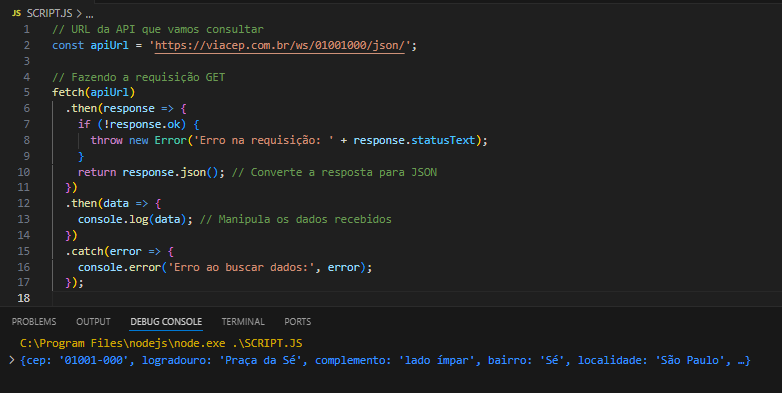
Neste exemplo, fazemos uma requisição GET para a URL da API. Utilizamos fetch para obter a resposta, convertemos a resposta para JSON e então manipulamos os dados recebidos. Caso ocorra um erro, ele é capturado e exibido no console.
Tratamento de Erros
O tratamento de erros é essencial ao trabalhar com APIs para garantir que a aplicação lida corretamente com situações inesperadas, como falhas de rede ou respostas inválidas.
Exemplo

Exemplo Prático
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="pt-br">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/style.css">
<script src="./js/script.js" type='module' ></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/FileSaver.js/2.0.0/FileSaver.js" integrity="sha512-UNbeFrHORGTzMn3HTt00fvdojBYHLPxJbLChmtoyDwB6P9hX5mah3kMKm0HHNx/EvSPJt14b+SlD8xhuZ4w9Lg==" crossorigin="anonymous" referrerpolicy="no-referrer"></script>
<title>Estudo de API com JavaScript</title>
</head>
<body>
<main class="container">
<h1 class="title">Sistema de Cadastro</h1>
<div class="row">
<div class="inputbox">
<input type="text" id="nome" required>
<label for="nome">Nome</label>
</div>
<div class="inputbox">
<input type="text" id="email" required>
<label for="email">Email</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="inputbox">
<input type="text" id="cep" required>
<label for="cep">CEP</label>
</div>
<div class="inputbox">
<input type="text" id="endereco" required>
<label for="endereco">Endereço</label>
</div>
<div class="inputbox">
<input type="text" id="numero" required>
<label for="numero">Número</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="inputbox">
<input type="text" id="bairro" required>
<label for="bairro">Bairro</label>
</div>
<div class="inputbox">
<input type="text" id="cidade" required>
<label for="cidade">Cidade</label>
</div>
<div class="inputbox">
<input type="text" id="estado" required>
<label for="estado">Estado</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<button id="salvar">Salvar</button>
</div>
</main>
<footer>
Aula de API © 2024
</footer>
</body>
</html>
CSS
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-family: 'Poppins', sans-serif;
}
body {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
min-height: 100vh;
background-color: rgb(4, 49, 123);
}
.container {
flex-grow: 3;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
width: 80%;
padding: 20px;
gap: 40px;
}
.title {
font-size: 40px;
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
}
.row {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fit, minmax(200px, 1fr));
gap: 40px;
}
label{
color: white;
}
.inputbox {
position: relative;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column-reverse;
height: 40px;
}
.inputbox input {
background-color: #f2e48e;
}
button {
cursor: pointer;
justify-self: center;
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
background-color:#a1f496;
font-size: 20px;
}
footer {
color: white;
padding-bottom: 20px;
}
JAVASCRIPT
const eNumero = (numero) => /^[0-9]+$/.test(numero);
const cepValido = (cep)=> cep.length == 8 && eNumero(cep);
const pesquisarCep = async ()=>{
const cep = document.getElementById('cep').value.replace('-','');
const url = `https://viacep.com.br/ws/${cep}/json/`;
if(cepValido(cep)){
const dados = await fetch(url);
const endereco = await dados.json();
if(endereco.hasOwnProperty('erro')){
document.getElementById('endereco').value = 'CEP não foi encontrado!'
}else{
preencherFormulario(endereco);
}
}else{
document.getElementById('endereco').value = 'CEP incorreto!';
}
}
const preencherFormulario = (endereco) =>{
document.getElementById('endereco').value = endereco.logradouro;
document.getElementById('bairro').value = endereco.bairro;
document.getElementById('cidade').value = endereco.localidade;
document.getElementById('estado').value = endereco.uf;
}
document.getElementById('cep').addEventListener('focusout', pesquisarCep)
function salvarDados(){
const cadastro = 'Cadastro'
const nome = document.getElementById('nome').value;
const email = document.getElementById('email').value;
const logradouro = document.getElementById('endereco').value;
const bairro = document.getElementById('bairro').value;
const localidade = document.getElementById('cidade').value;
const endereco = document.getElementById('estado').value;
const numero = document.getElementById('numero').value;
const cep = document.getElementById('cep').value;
var blob = new Blob([`${nome} - ${email} - ${logradouro} - ${bairro} - ${localidade} - ${endereco} - ${numero} - ${cep}`],
{type: 'text/plain: charset=utf-8'}
);
saveAs(blob, cadastro + '.txt');
limparFormulario();
}
document.getElementById('salvar').addEventListener('click', salvarDados)
function limparFormulario(){
document.getElementById('nome').value ='';
document.getElementById('email').value ='';
document.getElementById('endereco').value ='';
document.getElementById('bairro').value ='';
document.getElementById('cidade').value ='';
document.getElementById('estado').value ='';
document.getElementById('numero').value ='';
document.getElementById('cep').value ='';
}Conclusão
Trabalhar com APIs em JavaScript é uma habilidade essencial para desenvolvedores web. Utilizando fetch, async e await, podemos fazer requisições HTTP de forma eficiente e tratar respostas de maneira adequada. Além disso, o tratamento de erros garante que nossas aplicações sejam robustas e resilientes. Com essas ferramentas, é possível criar aplicações dinâmicas e interativas que se comunicam eficazmente com serviços backend.





21 Comments
Davi Da Silva Oliveira
Boa tarde! Professor Marcos mas um excelente trabalho. Obrigado
Felix Meyer
Thank you for sharing your precious knowledge. Just the right information I needed. By the way, check out my website at Webemail24 about Website Traffic.
Marcos
Thank you Felix, good studies and success!
alexistogel login
jpslot
I am sure this article has touched all the internet viewers, its really really
fastidious paragraph on building up new webpage.
Rtp Slot
dorahoki
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my website so i came to “return the favor”.I am
attempting to find things to enhance my web site!I suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas!!
pisang123
koitoto koitoto koitoto koitoto
Hi friends, how is all, and what you wish for to say on the topic of this article, in my view its genuinely remarkable designed for
me.
akartoto
jpslot jpslot jpslot jpslot jpslot
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to be actually something which I think I would
never understand. It seems too complex and extremely broad for me.
I’m looking forward for your next post, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
slot gacor hari ini
ohtogel ohtogel ohtogel ohtogel ohtogel
I think this is among the most significant information for me.
And i am glad reading your article. But wanna remark on some general
things, The website style is wonderful, the articles is really great :
D. Good job, cheers
dolantogel
singawin singawin singawin
Thanks for the good writeup. It actually was once a leisure account it.
Glance complex to more delivered agreeable from you! By the way, how can we communicate?
dultogel
sejitu sejitu sejitu
I am not sure the place you’re getting your information, however good topic.
I needs to spend some time learning more or working out more.
Thanks for wonderful information I was on the lookout for this information for my
mission.
Marcos
Thank you, good studies and success!
live streaming trans tv
Hi there, its good post on the topic of media print, we all know
media is a wonderful source of facts.
federasi bulu tangkis dunia
Great post. I used to be checking constantly this weblog and I’m impressed!
Extremely helpful information specially the final part 🙂 I
handle such info a lot. I was seeking this certain information for a
very lengthy time. Thanks and best of luck.
jarisakti138
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to revisit once again since I book marked it.
Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to
help others.
hercules 138
Exceptional post however I was wondering if you could write a litte more on this topic?
I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit more.
Cheers!
paito harian hk
It’s an amazing article in support of all the internet
visitors; they will obtain benefit from it I am sure.
idola88
I love it when individuals come together and share
thoughts. Great blog, stick with it!
cocinadelmundospices
It’s going to be ending of mine day, however before end I
am reading this great piece of writing to increase my
knowledge.
geinteriorismo
My brother recommended I might like this website. He was entirely
right. This post actually made my day. You can not imagine simply how much time
I had spent for this information! Thanks!
luubet login
Good site you have here.. It’s hard to find high-quality writing like yours nowadays.
I honestly appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Greaternewburyportfamilies
Thanks very nice blog!